What is an ECG?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a non-invasive and rapid test used to evaluate heart rate. With each heartbeat, an electrical impulse travels through the heart and triggers a contraction causing blood to pump from the heart. During the test, the ECG machine registers electrical signals traveling through the heart and creates a chart showing the characteristics of cardiac activity. ECG is commonly used to diagnose heart problems such as arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, hypertrophy of the heart muscle and other heart disease.
How does an ECG record the electrical activity of the heart?
The ECG records the electrical activity of the heart by using electrodes placed on the skin that detect the electrical impulses generated during each heartbeat. Electrodes are usually placed at certain points on the skin of the chest, arms, and legs, and then connected to an ECG machine. The electrical signals produced by the heart are visualized on the recording as wavy lines (Pallas, QRS complex, T wave) that have a certain power (voltage) and length of duration.
The electrical impulse begins in the sinoatrial (SA) node and spreads through the atria, causing their contraction, which is represented by the P wave. The impulse reaches the atrioventricular (AV) node, where a pause occurs, allowing the blood to enter the ventricles, which is seen as a flat line after the P wave (PQ segment) and before the QRS complex. The QRS complex represents the electrical impulse traveling from the AV node through the Purkinje fibers to the myocardial cells, resulting in simultaneous ventricular contraction. The ST segment follows the QRS complex as a flat line and is followed by the T wave, which represents the ventricles returning to a resting state. This represents one cardiac cycle or one heartbeat, which repeats at regular intervals.
An ECG provides information on the heart rate (number of beats per minute), rhythm (regular or irregular), size and position of the chambers, strength and timing of the electrical impulses passing through each part of the heart. This information is used for diagnosing heart conditions.
When is an ECG used?
An ECG is used in various situations to assess cardiac activity and diagnose heart problems, which can help in planning further treatment and therapy. Here are some common situations in which an ECG may be used:
Assessment of cardiac function in emergencies
An ECG can be used in emergency situations such as a heart attack or other acute cardiac events to quickly assess the patient’s cardiac function.
Evaluation of patients with cardiac symptoms
If the patient has symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, rapid pulse or irregular heart rhythm, dizziness or loss of consciousness an ECG is used to identify potential heart problems.
Diagnosing heart problems
An ECG can be used to diagnose heart problems such as arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, hypertrophy of the heart muscle, coronary heart disease and other heart conditions.
Regular check-ups
Electrocardiograms are often used as part of a routine assessment of cardiac function during regular check-ups with a doctor or in hospitals.
Monitoring of cardiac conditions
Conditions such as arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy, coronary artery disease, heart attack, heart failure, heart valve diseases, and congenital heart defects can be monitored using an ECG.
Monitoring of heart function during treatment
ECG can be used to monitor the effectiveness of medications and other treatments for heart problems.
Cardiovascular risk assessment for heart disease
In individuals with high blood pressure, diabetes, elevated cholesterol, obesity, or a family history of heart disease.
Examination for certain medical conditions
An ECG can be used to assess patients with certain medical conditions, such as lung or thyroid diseases, which can have an impact on cardiac function or as part of preoperative preparation for patients.
In summary, an ECG is recommended in various situations to assess the cardiac function of patients and identify potential heart problems. This information can help in planning further treatment and therapy.

Which cardiac conditions require an ECG?
An ECG is commonly used for diagnosing and assessing cardiac conditions that can impact heart function and lead to heart problems, as well as monitoring treatment effectiveness and planning further care. Some of these conditions include:
Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias are irregular heart rhythms that can be caused by a variety of factors, including heart disease, stress, anxiety, the use of certain medications, and more. An ECG is used to assess the type and severity of arrhythmias
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction (heart attack) is an emergency condition that occurs when blood flow through the heart is blocked, which can cause damage to the heart muscle. An ECG is commonly used to diagnose myocardial infarction and monitor cardiac function during recovery.
Coronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease is a condition that occurs when the arteries that bring blood to the heart narrow or block, which can lead to a heart attack or other heart problems. ECG can be used to assess heart function and identify heart problems that are associated with coronary heart disease.
Hypertrophy of the heart muscle
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a condition in which the heart muscle becomes too large and thickened, which can make cardiac function difficult. An ECG can be used to assess the severity of hypertrophy of the heart muscle.
Other cardiac conditions
ECG can be used to diagnose and assess the severity of other heart conditions, such as heart failure, ventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and others.
Which abnormalities can be diagnosed with an ECG?
An ECG is a test used to assess cardiac activity and diagnose heart problems. Some of the abnormalities that can be diagnosed with an ECG:
- An irregular heart rhythm or palpitations that can cause symptoms such as rapid pulse, shortness of breath, fatigue and other symptoms.
- Limited blood flow to the heart can cause symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath and fatigue.
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack) which can cause symptoms such as severe chest pain, shortness of breath and fatigue.
- Hypertrophy of the heart muscle can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and low blood pressure.
- Heart failure, ventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and other problems.
How can an ECG help identify the cause of cardiac symptoms?
Cardiac symptoms commonly associated with heart problems include chest pain, shortness of breath, irregular heart rhythm, and fatigue. Here are a few ways in which an ECG can help identify the causes of these symptoms:
Heart rhythm assessment
An ECG can help assess heart rhythm and determine if there is an irregularity in heart rhythm that may be caused by arrhythmia.
Identification of cardiac ischemia
Cardiac ischemia occurs when the heart doesn’t receive enough oxygen, which can lead to chest pain and other symptoms. An ECG can detect changes in the electrical activity of the heart that indicate cardiac ischemia.
Evaluation of cardiac damage
If the heart is damaged due to a heart attack or other heart problem, an ECG may show changes in the electrical activity of the heart that indicate damage to the heart tissue.
Assessment of electrical conductivity of the heart
An ECG can help assess the conductivity of electrical signals through the heart, which can detect blockages or other problems in the conduction of electrical signals
Evaluation of cardiac hypertrophyv
An EKG can detect an increase in the thickness of the heart walls, known as hypertrophy. This can be caused by high blood pressure or other heart conditions.
Based on the results of the ECG test and other diagnostic tests, the doctor can make a diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment for the cardiac symptoms.
Which healthcare professionals perform an ECG?
The ECG test is usually performed in hospitals, clinics, and doctors’ offices, and can be performed by the following healthcare professionals:
- Cardiologists are doctors specialized in diagnosing and treating heart disease. They are trained to interpret ECG and recognize abnormalities in heart rhythm, heartbeats, and other parameters.
- ECG technicians are trained to prepare patients for the ECG test, set up electrodes and perform an ECG test. They work under the supervision of cardiologists or other medical staff.
- Nurses can perform an ECG test, especially in outpatient or clinical settings. They are trained to place electrodes, perform an ECG test, and prepare a report for a doctor.
- General practitioners can perform an ECG test in their offices. They may use ECG for early detection of heart problems or to assess the condition of patients with cardiac symptoms.
It is important to note that the ECG test must be performed by trained medical personnel to ensure an accurate interpretation and diagnosis. The doctor who evaluates the results of the ECG test must be trained in the interpretation of the electrocardiogram.
What is the role of a cardiologist in interpreting ECG results?
Cardiologists are doctors specialized in diagnosing and treating heart diseases, including the interpretation of ECG (electrocardiogram) results. A cardiologist is trained to recognize abnormalities in heart rhythm, heartbeats, and other parameters provided by an ECG test. They are able to assess and diagnose various heart problems that can be identified through an ECG test, including cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, heart blockages, heart hypertrophy, and other heart conditions.
Cardiologists are also able to evaluate the results of the ECG test in the context of the patient’s overall clinical. For example, a cardiologist will consider the patient’s symptoms, medical history, previous diagnostic tests, and other factors before making a diagnosis based on the ECG test. The cardiologist will also consider whether further testing or evaluation is required, including heart ultrasound , CT coronarography or other diagnostic tests.
It is important to note that an electrocardiogram is not the only test used to assess heart function and diagnose heart problems, although it can be useful as a first step in evaluating heart function. A cardiologist will usually combine ECG test results with other tests and physical examination to make a diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment.
How does an ECG work?
An electrical signal travels through the heart, resulting in changes in the electrical field in the body. These changes can be detected by electrodes and are converted into a graphical display on an ECG machine. The graph shows different waves, segments and intervals representing different stages of cardiac activity. Based on these waves and other characteristics of the ECG, doctors can assess heart rhythm, heart rate, heart rate, duration of heartbeats, and other characteristics of cardiac activity.
An electrocardiogram works by recording the electrical signals generated during heartbeats and converting them into a graphical display on an ECG machine, which helps doctors in assessing cardiac function and identifying any potential heart problems.
How are electrodes placed on the body?
An ECG uses electrodes that are placed on the patient’s skin to record the electrical activity of the heart. Typically, 10 electrodes are used, and they are placed on specific points on the patient’s chest, arms, and legs. The placement of the electrodes takes only a few minutes and does not cause any discomfort or pain.
The electrodes are often placed in a V shape on the chest, with 6 electrodes placed on the front of the chest in specific positions (precordial leads). An additional 4 electrodes are placed on the arms and legs – two electrodes on the left arm, one on the right arm, and one on the right leg (standard leads). The electrodes are connected to the ECG machine via cables.
It is important to properly position the electrodes to obtain an accurate ECG recording. Doctors will usually check the placement of the electrodes before starting the test to ensure that everything is correctly positioned.
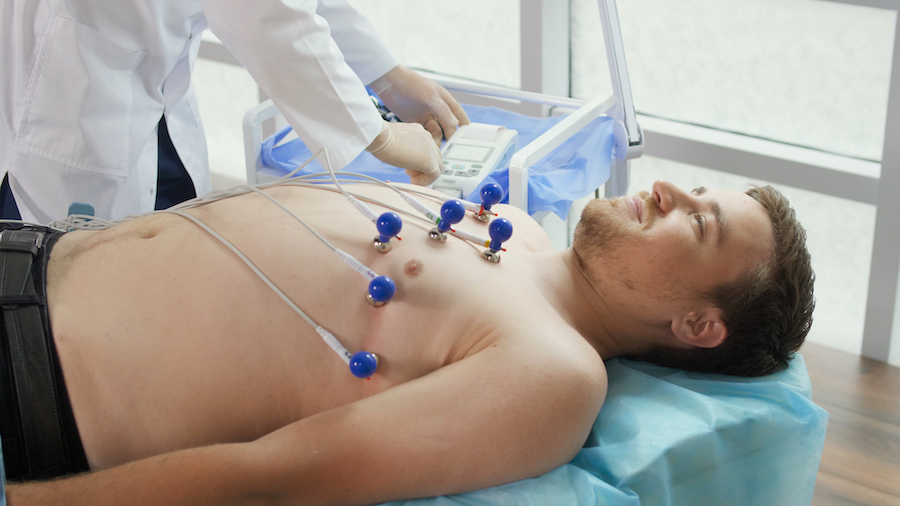
How does an ECG measure and record the electrical signals of the heart?
The process of measuring and recording the electrical signals of the heart via ECG involves several stages, which including:
- Preparation – before starting the test, the patient usually lies on his back while the electrodes are attached to specific points on the chest, arms and legs.
- Recording the electrical signals – during the heart cycle, an electrical signal is generated in the sinus node of the heart and travels through the heart. The electrodes on the patient’s skin detect these electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the EKG machine.
- Converting electrical signals into a graphical display – The electrical signals are converted into a graphical display on an ECG machine, which shows waves, segments and intervals representing different stages of cardiac activity.
- Interpretation of the results – A doctor interprets the results of the ECG test to assess cardiac function and identify possible heart problems. Based on the waves, segments, and intervals on the ECG, the doctor can assess the heart rhythm, heart rate, duration of each heartbeat and other characteristics of cardiac activity to evaluate cardiac function and identify possible heart problems.
How do I prepare for an ECG test?
There is no special preparation required for an ECG test, but there are a few things you can do to make the test easier:
Dress comfortably
During the ECG test, you will be asked to take your clothes off from the waist up and avoid tightening stockings or thicker longs because the electrodes are placed directly on the skin.
Remove jewelry
Before starting the test, remove jewelry, watches, bracelets, and other metal objects from your body, as they can affect the quality of the signal and interfere with the test.
Prepare for electrode placement
Avoid using oily lotions as they can make it difficult for the electrodes to stick to your skin. Prior to electrode placement, hair may need to be removed from the areas where the electrodes will be attached. If you have long hair on your chest or arms, you may need to trim or shave it before the test.
Avoid smoking and intense physical activity before the test
This can affect heart function and make it difficult to diagnose any heart problems.
Tell your doctor about medications, supplements and vitamins you are taking
Some medications, such as beta blockers, may affect heart function and interfere with the test, so you may need to temporarily discontinue them before the test.
Tell your doctor if you have a pacemaker
In that case, the electrodes will need to be placed in different locations on your body.
Who shouldn’t take an ECG test?
An ECG (electrocardiogram) is a relatively simple and safe test that can usually be done on most patients. However, there are certain conditions that can affect the results of the ECG test or pose a risk to the patient, so in these situations ECG is not recommended or must be done under special conditions.
Skin infection
If the patient has a skin infection in the places where the electrodes should be placed, the ECG test may be postponed until the infection is heald. Additionally, certain skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis can affect the signal quality on the EKG.
Pacemaker
If the patient has an implanted pacemaker, the electrodes cannot be placed over the pacemaker, as this can cause irregular signals on the ECG. Instead, electrodes must be placed in other places on the body. .
Severe respiratory insufficiency
If a patient has severe respiratory insufficiency, ECG recording may be challenging as the patient cannot inhale and exhale in a regular rhythm.
If the patient has any of these conditions or other medical conditions that the doctor should be aware of, it is important to inform the doctor before the electrocardiogram test. Your doctor will provide further instructions on whether there are any contraindications or recommendations to follow before or during the ECG test.
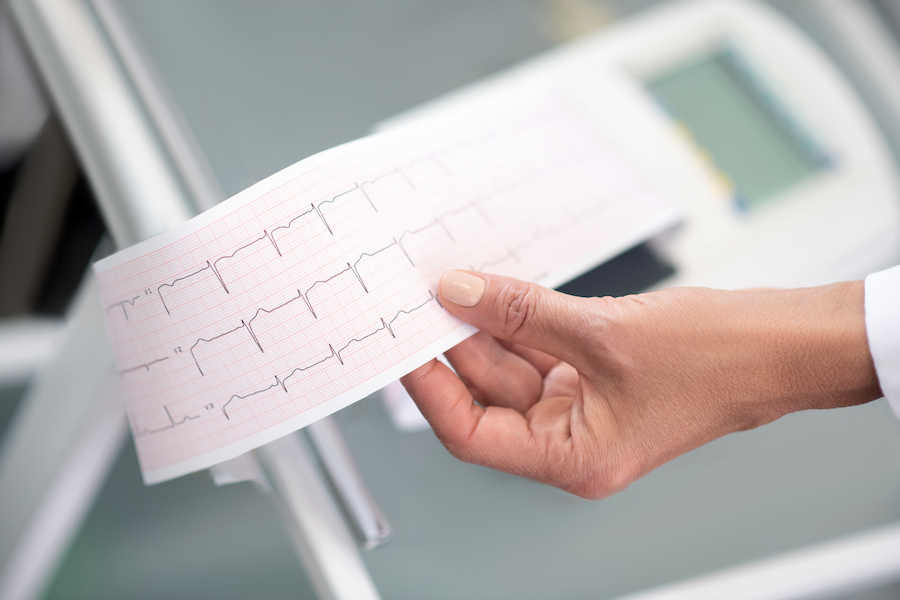
What kind of results do you get and what do those results mean?
The electrical signals produced by the heart are visualized on the EKG recording as wavy lines (P wave, QRS complex, T wave) with specific voltage and duration.
Normal ECG results can vary depending on the individual and the condition of the heart. However, there are several characteristics that are considered normal for most people. Here are a few of them:
Regular heart rhythm – consistent heartbeats at intervals of approximately 0.6-1.0 seconds.
Heart rate (frequency) – the number of beats per minute, typically between 60-100.
P wave, QRS complex, T wave have specific voltage and duration that are considered normal. The PQ segment and ST segment are on the isoelectric line. The normal P-R interval lasts between 0.12 and 0.20 seconds. The normal QTc interval for men is less than 450 ms, and for women, it is less than 470 ms.
It’s important to note that these parameters serve as general guidelines, and the final interpretation of ECG results will depend on the individual characteristics of each person.
Abnormal ECG (electrocardiogram) results indicate some changes in heart function, which may indicate various heart problems. Here are a few possible abnormalities that can be observed via ECG: arrhythmias, heart blockages, ST segment and T wave changes, heart hypertrophy, myocardial infarction.
This can be seen on the ECG as changes in the ST segment and the QRS complex.
It is important to note that these parameters represent only some of the possible abnormalities that can be observed on the ECG. If abnormalities are detected on the ECG, the patient will most likely be referred for further diagnostic and evaluation, which may include Holter monitoring of ECG, heart ECHO, CT coronarography.

Why is it important to have a discussion with a doctor regarding the findings of an ECG test?
The significance of discussing the results of an ECG test with a doctor is that it can help clarify any questions or concerns you have about the test and its findings. The doctor will be able to explain the meaning of any abnormalities observed on the electrocardiogram and how they may impact your health.
The conversation with the doctor can assist in planning the next steps in assessing your heart health, including additional diagnostic tests and treatment. This is because an ECG can provide only limited information about heart function as it captures a snapshot of your heart’s activity during a very brief period. If you have cardiac symptoms that come and go, a regular ECG may not detect the problem. In such cases, the doctor may recommend wearing a small portable ECG monitor such as a Holter monitor, which can be worn for up to two days, or event monitors, which can record your heart activity for weeks.
There are also heart disorders that cannot be observed during the work of the heart in peace, so your doctor may recommend a heart load test (ergometry). Additionally, the doctor may refer you for an echocardiogram (ultrasound) or CT scan (scanner) of the heart.
The doctor will be able to explain the options for further assessment and treatment and help you understand the benefits and limitations of each approach.
Having a conversation with your doctor is crucial in understanding your heart condition and receiving appropriate treatment.
When should I expect to receive the test results?
The timeframe for receiving the results of an electrocardiogram (ECG) test can vary depending on several factors, including the availability of equipment and healthcare professionals, the number of patients awaiting testing, and the urgency of the situation.
If urgent testing is required due to symptoms of heart problems, such as chest pain or difficulty breathing, an ECG test may be performed immediately upon arrival at the emergency department. In these situations, a prompt diagnosis and treatment can be crucial for the patient’s recovery.
If the ECG test is part of a regular physical examination or routine cardiac check-up, it is usually scheduled in advance and can be performed on the same day or within a few days.
In some cases, patients may undergo ECG testing as part of an outpatient or hospital procedure, such as preoperative preparation or during heart disease treatment.
What heart conditions require immediate medical attention?
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should seek urgent medical attention.
- Symptoms of myocardial infarction (heart attack) include chest pain, which can radiate to the arms, neck, back or stomach, shortness of breath, nausea and sweating.
- Symptoms of angina pectoris include chest pain or discomfort, which may be accompanied by a feeling of pressure or tightness, usually lasts for a few minutes
- Symptoms of arrhythmia include palpitations, a sensation of skipped heartbeats, dizziness, shortness of breath and loss of consciousness.
- Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism include difficulty breathing ,shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing up blood, rapid heartbeat and dizziness.
- Symptoms of an aortic aneurysm include sudden abdominal or chest pain, feeling weak, fainting, and shortness of breath.
Emergency medical intervention can be key in preventing serious consequences and improving outcomes.
When to consult a doctor after an ECG test?
You should contact a cardiologist to clarify your concerns and get a more detailed assessment of your heart health if you don’t have symptoms but have concering ECG test results.
Also, if you notice any symptoms or signs of a heart problem such as:
- Chest pain – if you have chest pain, especially if it spreads to the arm, neck or back
- Shortness of breath – Difficulty breathing
- Weakness or dizziness – If you feel weak or have episodes of fainting.
- Irregular heart rhythm – if you notice that your heart is skipping or beating too fast
- Swelling of the legs, feet and ankles
It is important to keep in mind that an ECG test can only provide limited information about the condition of the heart, and in order to make an accurate diagnosis and plan treatment, additional tests and consultations with a specialist may be required. Some of the additional tests are: ECG holter, Load Test, Heart ECHO, CT coronarography, etc


